| |
Bearing Circle and Azimuth Circle
Components
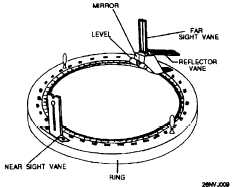
Figure 2-13. Parts of a bearing circle.
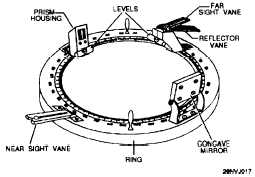
Figure 2-14. Parts of an azimuth
circle.
Figure 2-13 is a diagram of a
bearing circle and figure 2-14 is a diagram of an azimuth circle. The
table below lists the major parts and functions of each of these circles.
Part
Bearing
A z i m u t h
Function
Circle
Circle
Ring
Yes
Yes
Fits upon a 7 ½ inch gyro repeater.
Sight Vanes
Allow the observer to take bearings of objects by
aligning the two vanes to the object. The near vane
contains a peep sight while the far vane contains a
Yes
Yes
vertical wire. The far vane is mounted on top of a
housing that contains a reflective mirror inside
enabling the observer to read the bearing from the
reflected portion of the compass card.
Reflector Vanes
Allow the observer to observe azimuths of celestial
bodies (stars and planets) at various altitudes by
Yes
Yes
picking up their reflection in the black mirror.
When the body is observed, its reflection appears
behind the vertical wire in the far vane.
Levels
Yes
Yes
Indicate if the ring is level with the horizon.
NOTE: Bearings read when the ring is not level
are inaccurate.
Concave Mirror
Prism Housing
NO
NO
Yes
Yes
Reflects the Sun’s rays onto the prism housing on
the other side of the ring when the observer is
taking an azimuth of the Sun.
Directs the beam of light from the concave mirror
downward in a narrow beam onto the compass card
enabling the observer to read the azimuth to the
Sun.
2-24
|