| |
10-59.
What is the total declination
interpolation correction?
1.
10.7'
2.
20.5'
3.
23.0'
4.
26.3'
10-60.
What is the Hc (Tab)?
1.
42°27.3'
2.
41°38.1'
3.
40°48.5'
4.
40°44.4'
10-61.
What is the Hc (Comp)?
1. 41°16.0'
2.
41°18.0'
3.
41°17.6'
4.
41°15.7'
10-62.
What is the intercept?
1.
22.4 miles away
2.
22.4 miles towards
3.
16.2 miles away
4.
16.2 miles towards
10-63. What is the Zn?
1.
139.2°
2.
139.5°
3.
138.4°
4.
140.2°
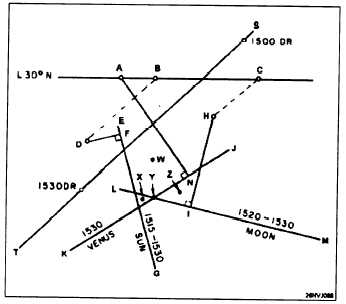
Figure 10-G
IN ANSWERING QUESTIONS 10-64 THROUGH 10-70
REFER TO FIGURE 10-G. FIGURE 10-G
PERTAINS TO A CELESTIAL FIX OBTAINED BY
THE INTERSECTION OF THREE LINES OF
POSITIONS. FIGURE 10-G SHOWS HOW (UNDER
IDEAL CONDITIONS) A FIX CAN BE OBTAINED
DURING THE DAYTIME BY OBSERVING THE SUN.
MOON, AND VENUS. THE SIZE OF THE
RESULTING TRIANGLE HAS BEEN ENLARGED IN
RELATION TO THE REST OF THE DIAGRAM
STRICTLY FOR ILLUSTRATIVE PURPOSES.
10-64.
10-65.
10-66.
10-67.
10-68.
10-69.
10-70.
What do points A, B, and C
represent?
1.
Known positions
2.
Assumed positions
3.
Altitude intercepts
4. Azimuth intercepts
What line represents the true
azimuth of a celestial body?
1.
B-D
2. E-G
3. H-I
4.
S-T
An altitude intercept is
represented by what line?
1. A-N
2. C-H
3. K-J
4. S-T
An advanced line of position is
represented by what lines?
1. B-D and C-H
2.
D-F and H-I
3.
E-G and L-M
4.
K-J and S-T
The 1530 fix should be indicated
as being at what point?
1.
W
2.
X
3.
Y
4.
Z
Which line of position, if any,
did NOT need to be advanced?
1. Moon
2.
Sirius
3.
Venus
4. None
If a celestial fix results in a
small triangle the fix should be
marked in the center.
1.
True
2.
False
65
|