| |
Atmospheric Pressure
Weight
The layer of atmosphere that surrounds us exerts a pressure of
approximately 15 pounds per square inch at sea level. The weight of the
atmosphere varies with the presence of water vapor as well as with
temperature and height above sea level. Variations in atmospheric
pressure are measured by an instrument called a barometer.
Aneroid
Barometer
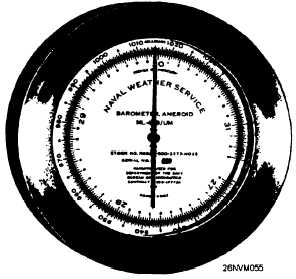
The aneroid (dry or no fluid) barometer (ML-448) (fig. 10-3) needs no
correction except for altitude. It contains a small metallic cell, called a
syphon cell, which encloses a partial vacuum. As atmospheric pressure
increases, the syphon cell contracts; as pressure decreases it expands.
Figure 10-3. Aneroid barometer.
As the syphon cell expands and contracts, it communicates motion to an
indicating pointer on a graduated scale.
The aneroid barometer (ML-448) is graduated in inches of mercury and
in millibars (mb). Both inches and millibars are measurements of the
weight of the atmosphere at a given time or point. The average
atmospheric pressure at Earth’s surface is 29.92 inches or 1013.2
millibars.
10-11
|