| |
STORAGE BY SIZE.— The principle of
storage by size is that the storage or warehouse
layout is determined by the size and bulk of the
material being stored. In addition to size and bulk,
some factors to be considered are the anticipated
stock level for an item, the frequency of receipt
and issue, and the difficulty in moving the item.
Storing items by size does not always permit the
fast-moving items to be closest to the issue point.
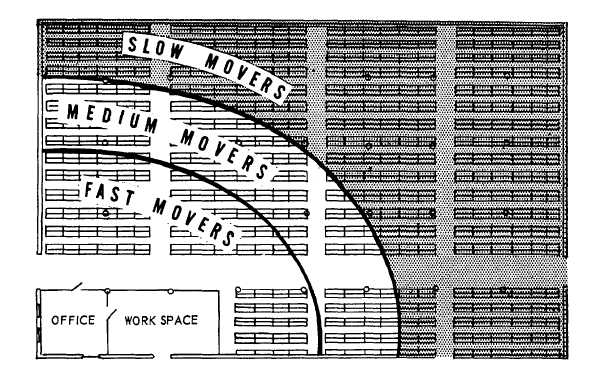
POPULARITY STORAGE.— In popularity
storage, the items with the highest turnover rate
are stored as close as possible to the receipt and
breakout point. Figure 7-6 illustrates this method
of storage. Popularity storage is generally con-
sidered the best method of storage since it allows
quick access to fast-moving stores. Experience and
conditions show that a combination of the various
methods of storage will better suit your needs.
STORAGE DETERMINED BY MATERIAL
CHARACTERISTICS.— The material character-
istics of some items make it necessary to provide
special storage areas for them. Two examples of
this are hazardous materials, which must be stored
in an area where the material hazard is controlled
or eliminated, and pilferable items, which must
be stored in buildings or areas where security for
the items can be maintained.
WORK AREAS.— The storage layout of a
warehouse should contain provisions for an of-
fice and work area. This space should be kept to
a minimum and not exceed an area larger than
that required to handle an average workload. The
office and work area should be located as close
as possible to the main access door of the
warehouse.
Aisles
One of the most important features of good
warehousing is aisle arrangement. Five types of
aisles are used in Navy warehouses: main, cross,
personnel, fire, and service.
MAIN AISLES.— The main aisles serve as the
lifeline or arteries of a warehouse. Main aisles
generally run the length of the building and should
be kept clear at all times. They are located so that
they give direct access to shipping and receiving
platforms, doorways between sections, and in
multistory buildings they give access to elevators
and conveyors. The number of main aisles in a
section or on a floor of a multistory building
depends on the number of communicating doors
and elevators required to move material in and
out of the area. The number of main aisles is also
determined somewhat by the size of the lots and
Figure 7-6.—Popularity system of storage.
7-19
|