To establish a system of controls that will be of
and if the expenses were recognized and recorded
against the OPTAR at the time they occurred instead
maximum value to commanders. Commanders
of when they were requisitioned or when payment
use these controls to assure that resources are
was made. The responsible commander's flexibility
u s e d e ff e c t ive l y a n d e ffi c i e n t l y i n t h e
to shift resources to meet these changing demands is
accomplishment of the mission of the activity.
greatly increased by the fact that his or her budget will
To furnish operating budget grantors and other
contain additional resources that were previously
levels of management, up to and including the
provided by individual allotments.
Navy Comptroller, that degree of financial
Four interrelated subsystems make up the RMS to
information necessary for effective coordination
meet the objectives of the DOD. They are as follows:
and control of resources.
Programming and budgeting
These objectives are achieved by implementation
Management of resources for operating units
of the planning, programming, and budgeting system
Management of inventory and similar assets
and the use of such functional terms as funds,
appropriations, expense operating budgets,
Management of acquisition, use, and disposition
responsibility centers, cost centers, expense
of capital assets
elements, and OPTARs. With an understanding of the
interlocking functions of all these factors, the fiscal
The first, third, and fourth items are applicable
side of supply becomes a clear and purposeful system.
primarily at the department, bureau, or inventory manager
The material presented in this chapter provides the
level. The SK would be most concerned with the second
necessary background information. Perhaps SKs may
item. Current guidelines for the management of resources
not be personally involved in the consolidation of
for operating units are found in Financial Management of
budget estimates; however, it will be helpful if they
Resources Operations and Maintenance (Shore
know how the process is carried out and how the
Activities), NAVSO P-3006, Financial Management of
action taken at higher levels may both depend upon
Resources Fund Administration (Operating Forces),
and affect what they do locally.
NAVSO P-3013-1, and Financial Management of
Resources Operating Procedures (Operating Forces),
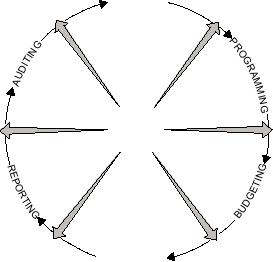
The RMS affects the entire management process
NAVSO P-3013-2.
in the DOD. The following paragraphs briefly define
steps in the management process. Figure 8-8 indicates
OBJECTIVES
the normal sequence of the steps in the management
cycle.
The basic objectives of the RMS, as applied to
operating units, are as follows:
Planning in DOD is concerned with developing
long- and midrange strategy and operational
To determine the cost of operation of an activity
concepts, objectives, and requirements based on
in terms of total resources consumed or applied.
continuously projected appraisals of the world
situation and on technological and intelligence
PLANNING
forecasts.
Programming is concerned with setting specific
5-year defense goals and the schedule for achieving
them, grouping functions and activities sharing the
same objectives into major programs, and estimating
resource requirements for each.
MANAGEMENT
ACTION
Budgeting is the function of formulating 1-year
projections of resource requirements for programs,
balancing priorities in the competition for limited
resources, and obtaining associated funds.
Accounting is the function of measuring the
results of performance (progress and status of
ACCOU TING
N
SKf08008
programs), usually in financial terms, both for
Figure 8-8.--Simplified Department of Defense management
functional areas and organizational units.
process.
8-10

